Contents
- 1 Handheld vs Desktop 3D Scanners: Selecting the Right Technology
- 1.1 Understanding Scanner Types
- 1.2 Handheld vs Desktop 3D Scanners: Comprehensive Analysis
- 1.3 Handheld 3D Scanners: Mobility and Flexibility
- 1.4 Desktop 3D Scanners: Precision and Consistency
- 1.5 Key Comparative Factors
- 1.6 Recommended Selection Criteria
- 1.7 Technology Integration Considerations
- 1.8 Conclusion
Handheld vs Desktop 3D Scanners: Selecting the Right Technology
In the evolving world of 3D scanning technology, professionals and enthusiasts face a critical decision: choosing between handheld and desktop 3D scanners. Each type offers unique advantages and limitations that can significantly impact scanning performance and project outcomes.
Understanding Scanner Types
3D scanners capture precise three-dimensional digital representations of physical objects, transforming them into detailed 3D models for various applications such as engineering, design, reverse engineering, and quality control.
Handheld vs Desktop 3D Scanners: Comprehensive Analysis
3D scanning technologies have evolved to offer two primary scanning configurations: handheld and desktop systems, each designed to address specific measurement and digitization requirements.
Handheld 3D Scanners: Mobility and Flexibility
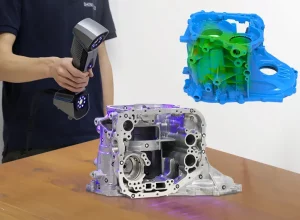
Handheld 3D scanners provide exceptional versatility for capturing complex or large-scale objects that cannot be easily positioned on a fixed platform. These devices leverage advanced optical and laser technologies to generate high-resolution 3D models with remarkable precision, typically offering accuracy ranges between 0.05mm to 0.5mm.
Desktop 3D Scanners: Precision and Consistency
Desktop scanners excel in capturing smaller objects with superior dimensional accuracy, making them ideal for industries requiring meticulous measurements such as industrial design, metrology, and quality assurance. These stationary systems often integrate automated turntable mechanisms, enabling comprehensive multi-angle object scanning with repeatability within micron-level tolerances.
| Scanner Type | Accuracy Range | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Handheld Scanners | 0.05mm – 0.5mm | Large objects, complex geometries |
| Desktop Scanners | 0.01mm – 0.1mm | Small precision parts, research |
Selection between handheld and desktop 3D scanners depends on specific project requirements, object characteristics, and desired measurement precision.
Handheld 3D Scanners: Mobility and Flexibility
Handheld 3D scanners represent a revolutionary approach to capturing three-dimensional digital representations of objects, offering unprecedented mobility and adaptability in various professional and industrial contexts. These sophisticated devices leverage advanced optical and sensor technologies to enable users to capture complex geometries that traditional stationary scanners cannot easily accommodate.
The primary advantage of handheld scanners lies in their ability to navigate around intricate objects, providing comprehensive scanning capabilities for large-scale artifacts, industrial components, archaeological findings, and anatomical structures. Unlike desktop scanners confined to fixed platforms, these portable devices empower users to scan objects in their natural environment, whether in expansive manufacturing facilities, remote archaeological sites, or medical research laboratories.
| Handheld Scanner Advantages | Potential Limitations |
|---|---|
| Portability and on-site scanning | Potential scanning accuracy variations |
| Ability to scan large/complex objects | Operator skill and technique dependent |
| Flexible positioning and accessibility | Higher initial equipment cost |
| Real-time data capture | Battery life and power management constraints |
Modern handheld 3D scanners incorporate sophisticated technologies such as structured light projection, laser triangulation, and photogrammetric techniques. These technologies enable precise depth mapping and surface reconstruction, compensating for potential mobility-related scanning challenges. Professional-grade devices often include integrated stabilization mechanisms, real-time error correction algorithms, and advanced calibration features to maintain high-precision measurements.
Key professional domains leveraging handheld 3D scanning technology include reverse engineering, quality control, medical prosthetics, cultural heritage preservation, and forensic investigation. The ability to capture detailed 3D representations rapidly and dynamically makes these devices invaluable tools for professionals requiring flexible, high-resolution digital documentation.
Desktop 3D Scanners: Precision and Consistency
Desktop scanners are stationary systems designed for high-precision scanning of smaller objects. They provide exceptional accuracy and repeatability, making them ideal for detailed measurements and quality control.
Key Comparative Factors
Scanning Accuracy
Desktop scanners typically offer higher accuracy (0.05-0.1mm) compared to handheld scanners (0.1-0.5mm). This precision makes desktop models superior for intricate engineering and medical applications.
Object Size Considerations
Handheld scanners accommodate larger objects like automotive parts, architectural elements, and full-body scans. Desktop scanners are best suited for smaller components such as mechanical parts, prototypes, and precise mechanical components.
Cost Analysis
Desktop scanners generally have lower initial costs but limited scanning volume. Handheld scanners require significant investment but offer greater versatility and scanning range.
Recommended Selection Criteria
- Choose handheld scanners for: Large objects, on-site scanning, diverse environments
- Choose desktop scanners for: Small, precise objects, laboratory settings, consistent measurements
Technology Integration Considerations
Modern scanning workflows often incorporate both technologies. Some professionals utilize handheld scanners for initial capture and desktop scanners for refined, high-precision refinement.
Conclusion
Selecting between handheld and desktop 3D scanners depends on specific project requirements, budget constraints, and desired scanning outcomes. Carefully evaluate your precise needs to make an informed decision.